The Global Options are settings that apply to all computers, regardless of their group membership. The global options are divided into the "General" and the "Heartbeat" settings, click the respective tab to access them.
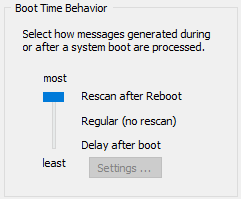
Boot Time Behavior
|
EventSentry monitors the event log when it is running. When the service is not running (such as when the system is being rebooted), it is unable monitor the event logs. Event log entries created while the service is stopped are not processed.
To avoid this problem you can configure EventSentry to look for events created after the service was last shut down by setting this feature to "most". Every time the service starts it scans the event log from the last checkpoint. This feature is also useful in determining if a server was rebooted.
Most: EventSentry will re-scan the event log and process events that occurred while the service was stopped.
Regular: EventSentry will monitor the event log right after the service was started, but will not process events that occurred while the service was stopped.
Least: EventSentry will ignore events that occurred for the first X seconds after the OS booted. For example, if EventSentry emails you a lot of events when a server is rebooted, then you can configure this feature to suppress events for a given amount of seconds. Click the "Settings" button to bring up the "Boot Delay Settings" dialog that lets you configure the interval and to which action types this feature applies to. |
Note: SMTP emails sent from a boot scan will have "[RESCAN]" appended to the subject.
|
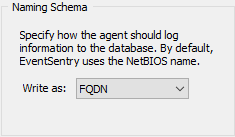
This option controls how hosts identify themselves in the web reports.
NetBIOS By default, computer names will appear with their NetBIOS names (e.g. SERVER1) in alerts and the web reporting.
FQDN Hosts will show up with their respective FQDN names instead (e.g. server1.yourdomain.local) of just the host name. Please note that you will have to restart the agent for this change to become effective.
Alias Forces hosts to show up with the name defined in the management console instead of their actual host name. This setting requires that at least one active IP address matches the IP address configured for the host name in an EventSentry group. This setting is useful for environments where hosts with identical names but from different sub nets connect to the same EventSentry database. When configured, also supports the $HOSTNAMEALIAS variable.
|
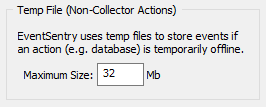
Temp File
|
Certain action types, including email, database and Syslog, have the ability to cache events when the configured server is temporarily unavailable. This setting allows you to configure the maximum amount of disk space that EventSentry will use in the system temp directory (%TEMP%) for caching events.
This setting also applies to the storage used for the summary actions. |
Maximum Notification Intervals
|
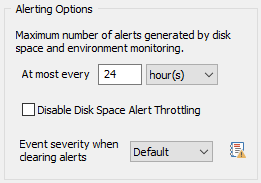
Many features, including environment monitoring, disk space and service monitoring write alert messages to the event log when a certain problem (e.g. low disk space, high environment temperature, etc.) is detected. To avoid the event log from being flooded with the same event pertaining to the same problem you can set a maximum notification interval here.
For example, if you set a maximum notification interval of 24 hours then a low disk space warning regarding drive C will only be logged once every 24 hours until the low disk space problem is resolved. |
Alert Clear Severity
|
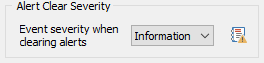
By default, performance & disk space monitoring features log events with the same event severity (as configured in the object) regardless of whether an issue has been detected or resolved. This is so that default event log filter rules process both alert & resolution identically.
Since this can both be confusing (an issue is resolved but logged as an "Error"), this setting overrides the default behavior and will log events that indicate that an issue has been resolved with the selected severity.
This setting only affects Performance Monitoring & Disk Space Monitoring. |
UTC Support
|
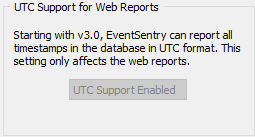
Starting with version 3.0, EventSentry can write all time stamps in the UTC time zone to the database. This is helpful for networks spanning multiple timezones, since the web reports can display all data in the local time zone of the currently logged on user.
UTC support is enabled by default for new installations, and can also be switched on for users upgrading from earlier installations. Once enabled, UTC support cannot be turned off again.
UTC only affects the web reports, alerts generated by the agents for example still use the time stamp from the local time zone the agent is located in.
|
Maintenance Schedules for Agents
|
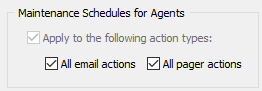
When maintenance schedules are created for a group or host, they only apply to heartbeat alerts generated by the Heartbeat Agent; any alerts (e.g. event log alert via email) are still sent out by an agent.
To suppress all email alerts during a maintenance schedule, check the "All email actions" check box; check the "All pager actions" check box to suppress all pager alerts.
Both check boxes are checked by default with new installations. |
Security Options
|
Agents: only store the group agent is a member of in local registry config By default all remote agents receive the full EventSentry configuration transmitted, including all groups and hostnames contained therein. This may not be desirable in situations where the same EventSentry configuration is used to monitor disparate & isolated networks, such as in MSP environments. Enabling this option ensures that a remote agent only stores the group data from the group it is a member of. |
EventSentry ships with a free Geolite city geolocation database which will supplement IP addresses with their corresponding geolocation. EventSentry includes this database, which is updated with every EventSentry version update that is released. The latest version of the database can also be downloaded from http://dev.maxmind.com/geoip/geoip2/geolite2/. Follow the steps below to update the geoip database:
1.In the management console, click on "Services"
2.Stop the "Network Services" service
3.Stop the "Collector" service if it is running
4.Replace the GeoIP database file with the latest version (mmdb format only!)
5.Start the "Collector" service again if it was running
6.Start the "Network Services" service
Utilizes three public black lists (OTX, Firehol, Blocklist.de) that are downloaded every 4 hours to identify potentially malicious IP addresses.If an API key is configured, then a black list from AbuseIPDB is downloaded (in addition to the 3 free blacklists) and a threat status of each IP address is also obtained from the AbuseIPDB web site in real time. See AbuseIPDB Pricing for more details, a free service with limited checks is available (1000 queries / day as of November 2020).
Custom Block List: In order to incorporate third-party block lists, save the blocked IPs in the following format to the file %SYSTEMROOT%\system32\eventsentry\temp\eventsentry_threatintel_custom.tmp. This file, when present, will be imported every time the other blacklists are downloaded:
IP;Confidence Score;Title
IP: IP Address
Confidence Score (optional): Number 0..100
Title (optional): Threat title or description
Example:
10.20.30.40;60;Port Scan
10.20.80.22;90;Web Attack,Port Scan,Spam
Optional fields can be omitted: "Confidence Score" defaults to 50 if not present, "Title" is set to "n/a" if not present. At minimum, one IP address per line must be specified.
The threat intelligence status can be used in event log filters and in the web reports to filter reports based on the threat status of an IP address.
Heartbeat Settings
Please see "Setting General Options" in the Heartbeat Monitoring chapter for more information on the general heartbeat settings.